OLI thermodynamic models
Aqueous (AQ) model
The AQ model is OLI's most widely used electrolyte thermodynamic framework. A fully speciated model with coverage of 80+ elements of the periodic table, for systems -50 to 300 C, 0 to 1500 bar, and up to 30 molal ionic strength. This is suitable for heavy brines, brackish water, slurries: anywhere where water (H2O) is dominant. This model assumes the presence of water.
OLI process technology
OLI as a property method
OLI's range of applicability extends to multi-stage calculations and also multi-unit processes with recirculation.
When you are using a commercial flowsheet simulator and would like to include OLI as a property method, you can! OLI is available as a property method in several flowsheet simulators by using one of OLI's Alliance Partner products.
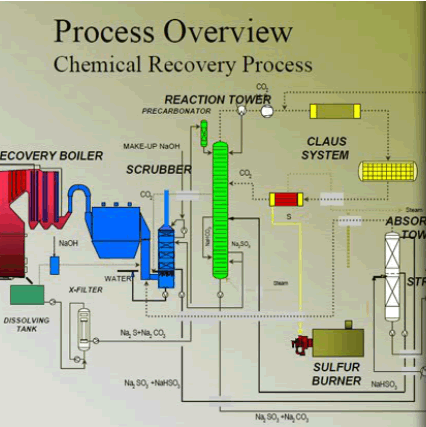
Electrolyte flowsheet simulation
For clients who have applications that are electrolyte-primary or electrolyte-only, or who require some of OLI's advanced simulation capabilities in either kinetics, mass transfer, or specialized units, OLI has developed OLI-only thermodynamics in an electrolyte flowsheet simulator.
OLI upstream technology
OLI's mineral scale prediction for the upstream has become the industry standard for scale analysis in new and existing assets. OLI's electrolyte thermodynamic framework offered a solid beginning. Building on the framework throughout the years, OLI has partnered with industry specialiists in oil and gas companies who have specified the requirements for state-of-the-art, specialized upstream calculations.
Presently, OLI is once again partnering with industry through a AQSim-, OLI- and Scaled Solutions-sponsored JIP, UltraHPHT. UltraHPHT is a project that combines experimental work and modeling work, in order to increase the accuracy of OLI simulations for the extremely high pressure / high temperatures of production environments today.
OLI for pipeline calculations
OLI can calculate scale appearance and disappearance lines within a pipeline, rigorously predicting scale behavior of fluids in pipelines. This is possible by partnering with Schlumberger and using the joint capabilities of OLI electrolyte thermodynamic model and Schlumberger's fluid flow model.
Mixed Solvent Electrolyte (MSE) model
The MSE model is OLI's newer model which has removed both concentration limit and the presence of water as limits to its simulation capability. The MSE model has coverage at 49% of the AQ databank and in addition, it contains many chemistries that cannot be simulated in the AQ model because they are beyond the AQ model's capability. The MSE model is recommended and preferred when your chemistry of interest contains significant amounts of highly miscible components such as HF, MEG, methanol, etc..
Solution thermodynamics Thermodynamics of corrosion
Kinetics of generalized corrosion
Localized corrosion
EVS
OLI's applied R & D into the science of corrosion began in 1995, building on the first step in understanding aqueous corrosion: the solution thermodynamics. OLI then added models for the thermodynamics of corrosion through the facility of Pourbaix Diagrams; a model for the kinetics of generalized corrosion by generating Polarization curves and also the partial anodic and cathodic processes that develop; a model for localized corrosion by calculation of corrosion potential versus repassivation potential, and a statistical model for calculating remaining asset life given pit depth versus time information.
OLI Technology
A summary of OLI core competencies